India–EU Seal Landmark Free Trade Deal: PM Modi Announces $100 Billion Boost & 10 Key Gains
India and the European Union have sealed a landmark free trade deal, PM Modi announces. Explore key benefits
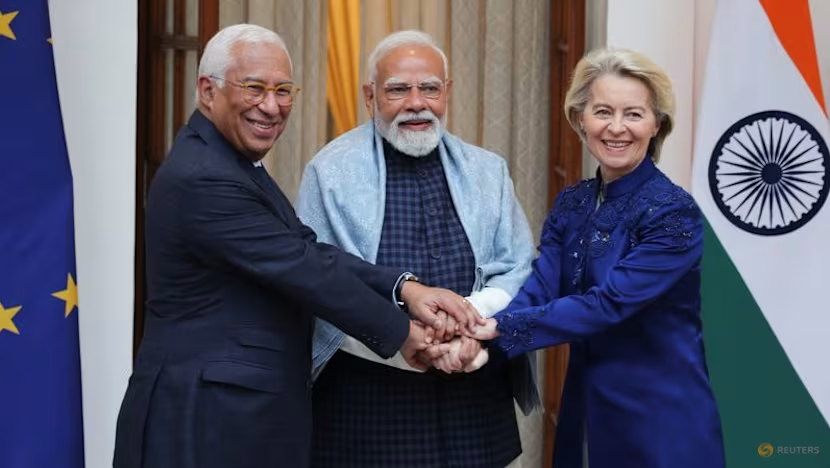
In a major geopolitical and economic breakthrough, India and the European Union have officially closed a ‘landmark’ free trade deal, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced, marking a transformative moment in bilateral relations between two of the world’s largest economic blocs. The agreement, years in the making, is expected to dramatically expand trade, unlock new investment flows, generate millions of jobs, and deepen strategic cooperation across technology, manufacturing, green energy, and digital services.
Calling it a “historic win for both India and Europe,” PM Modi said the deal reflects a shared commitment to open markets, resilient supply chains, and sustainable growth at a time of global economic uncertainty and shifting trade alliances.

The India–EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations began over a decade ago but stalled multiple times due to disagreements on tariffs, intellectual property rights, data protection rules, labor standards, and environmental safeguards. Talks were formally relaunched in 2022, gaining momentum as both sides sought to diversify supply chains and reduce dependence on a narrow group of trading partners.
The final agreement represents a strategic reset in India–EU ties and is being hailed as one of the most ambitious trade deals either side has concluded in recent years.
This landmark agreement opens a new chapter in India–EU relations. It will accelerate trade, boost innovation, create jobs, and strengthen people-to-people ties,” PM Modi said in his statement.
European Commission leaders echoed the sentiment, describing the deal as a “game-changer” that will link two dynamic markets representing nearly 1.8 billion people and over $20 trillion in combined GDP.
The India–EU FTA is being described as landmark for several reasons:
- Scale of Economic Impact:
The deal is expected to push bilateral trade beyond $120–150 billion annually over the next decade, up from current levels of around $135 billion. - Breadth of Coverage:
It goes beyond traditional tariff cuts to include digital trade, services, investment protection, sustainability standards, and intellectual property cooperation. - Strategic Timing:
The agreement comes amid global trade realignments, offering both sides a reliable and diversified economic partnership. - Job Creation Potential:
Analysts estimate the pact could create over 2 million jobs across manufacturing, services, logistics, and high-tech sectors.
One of the most significant elements of the deal is the phased elimination or reduction of tariffs on thousands of goods:
- EU concessions:
Lower duties on Indian textiles, garments, leather goods, pharmaceuticals, agricultural products, seafood, and automotive components. - Indian concessions:
Reduced tariffs on European automobiles, wines and spirits, high-end machinery, medical devices, chemicals, and renewable energy equipment.
This mutual tariff liberalization is expected to make Indian exports more competitive in Europe while providing Indian consumers and industries access to high-quality European goods at lower prices.

India’s globally competitive IT, fintech, healthcare, and professional services sectors stand to gain significantly.
- Easier movement of professionals between India and EU member states
- Recognition of professional qualifications
- Improved market access for Indian IT firms and startups
- Expanded cooperation in artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and data services
The services chapter is being seen as a major win for India, which has long pushed for better access to European service markets.
The deal includes robust investment protection provisions aimed at encouraging European companies to expand operations in India and Indian firms to invest in Europe.
Key features include:
- Transparent dispute resolution mechanisms
- Protection against arbitrary expropriation
- Clear rules for cross-border investments
- Support for joint ventures and technology transfers
European investments in India are expected to surge, particularly in manufacturing, clean energy, infrastructure, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics.
For the first time, India and the EU have agreed on a forward-looking digital trade framework that balances innovation with data protection.
Highlights include:
- Cross-border data flow facilitation
- E-commerce cooperation
- Cybersecurity collaboration
- Protection of consumer data
- Interoperable digital standards
This is expected to benefit India’s booming startup ecosystem and Europe’s tech-driven industries.
The agreement embeds sustainability as a core pillar, reflecting Europe’s green priorities and India’s climate commitments.
- Alignment with the Paris Agreement
- Commitments to reduce carbon footprints
- Cooperation on renewable energy and green hydrogen
- Labor rights and environmental safeguards
- Promotion of sustainable supply chains
Both sides emphasized that trade growth must be environmentally responsible and socially inclusive.
Export Growth:
Indian exporters in textiles, pharmaceuticals, gems and jewelry, seafood, chemicals, and engineering goods will gain preferential access to the EU market.

Job Creation:
Millions of new jobs are expected in export-oriented industries, logistics, and MSMEs.
Technology Transfers:
Enhanced cooperation with European firms will accelerate India’s move up the manufacturing value chain.
Supply Chain Resilience:
The deal reduces India’s dependence on a few major trading partners.
Access to a Massive Market:
European firms gain improved access to India’s 1.4 billion consumers.
Manufacturing Partnerships:
EU companies can leverage India’s cost-efficient manufacturing base.
Green Energy Opportunities:
European renewable energy firms will play a key role in India’s energy transition.
Geopolitical Influence:
Strengthening ties with India helps the EU expand its strategic footprint in the Indo-Pacific.
- Automobiles and EVs
- Renewable energy and green hydrogen
- Pharmaceuticals and biotechnology
- Textiles and apparel
- Information technology and AI
- Agriculture and food processing
- Logistics and ports
Each of these sectors is projected to see multi-billion-dollar investment inflows over the next decade.
Beyond economics, the deal carries enormous strategic weight.
At a time when global trade is being reshaped by geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and protectionist trends, the India–EU pact signals a strong commitment to multilateralism and rules-based trade.
For India, the deal strengthens its position as a key global manufacturing and investment destination. For Europe, it offers a reliable partner in Asia with a stable political environment and fast-growing economy.
Potential pressure on domestic industries from European imports
Impact on small farmers and MSMEs
Intellectual property rules affecting the pharma sector
Environmental compliance costs
- Labor and human rights standards
- Environmental commitments
- Market access enforcement
Governments on both sides have said safeguard mechanisms are in place to protect vulnerable sectors and ensure fair implementation.

- Legal scrubbing
- Ratification by the Indian Parliament
- Approval by the European Parliament
- Endorsement by EU member states
Officials estimate the FTA could enter into force within 12 to 18 months, with tariff reductions rolled out in phases over 5 to 10 years.
The India–EU FTA rivals some of the world’s biggest trade agreements in scale and ambition, comparable to:
- EU–Japan Economic Partnership Agreement
- Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
However, unlike RCEP, this pact includes strong digital trade and sustainability chapters, making it one of the most modern FTAs globally.
- Reshape global supply chains
- Strengthen India’s manufacturing base
- Accelerate Europe’s access to Asian markets
- Boost innovation and green technology cooperation
- Create long-term economic stability
If implemented effectively, the pact could serve as a blueprint for future trade agreements between emerging and advanced economies.
Read Also : Mumbai Weather Forecast Today: Dry Skies, 30°C Heat & Rising Air Quality Concerns in 2026